Fracture of the shoulder girdle
What are shoulder girdle fractures?
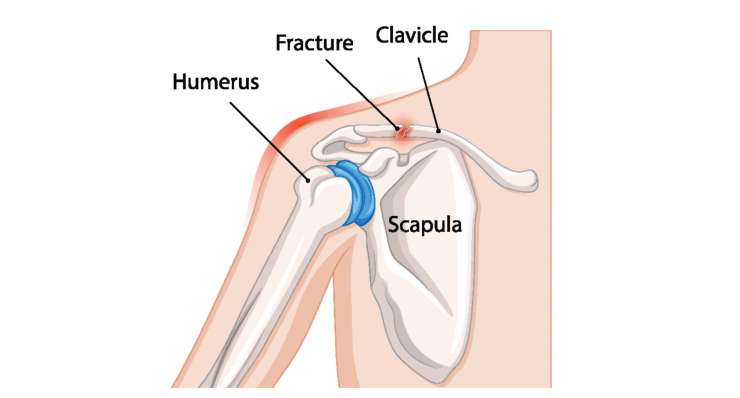
Shoulder girdle fractures are breaks in the bones that form the shoulder girdle. The shoulder girdle consists of the shoulder blade (scapula), the collarbone (clavicle), and the upper arm bone (humerus), which are connected to each other and form the shoulder joint.
Fractures of the shoulder girdle can be caused by a variety of factors, such as falls, accidents, or sports injuries. Symptoms of a fracture of the shoulder girdle can include pain, swelling, bruising, and limited mobility in the affected area.
It is important to see a doctor if you suspect a shoulder girdle fracture in order to obtain an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment can help ensure that the injury is treated more quickly and effectively and reduce the risk of complications.
Medical explanation
Fracture of the humeral head (proximal humerus fracture) and fracture of the collarbone (clavicle fracture)
Falls or other accidents can cause bone fractures in the area of the humeral head or collarbone. The complexity of the injuries ranges from undisplaced fractures with two fracture parts to severely displaced comminuted fractures. Accordingly, there are different treatment options. Fractures that are not displaced or only slightly displaced can be treated conservatively. After two weeks of immobilization in a sling, passive physiotherapy with increasing intensity is initially performed. The bone fracture is usually healed and stable after 6-8 weeks.
Severely displaced fractures are surgically repaired and fixed with plates or nails (osteosynthesis) to ensure anatomical position and good postoperative function. It is crucial to consider the biomechanics and function of the shoulder, including the affected soft tissues, as the surgical outcome depends on this.
If reconstruction is no longer possible due to the severity of the injury, the last alternative is to implant a fracture prosthesis in the humeral head. Depending on the quality of the rotator cuff and the age of the patient, an anatomical or inverse prosthesis is used.
In-patient stay
2–3 days
Follow-up treatment
In cases of surgically treated fractures, mobilization of the shoulder can begin immediately after surgery to counteract stiffening of the joint. The entire follow-up treatment for osteosynthesis of the shoulder girdle or fracture prosthesis can take 3-6 months to restore optimal function.
Comprehensive information on other shoulder and elbow conditions and treatment options can be found in the complete range of treatments offered by Prof. Dr. med. Frank Martetschläger.
